Table of Contents
5.5.2. Fine-tuning the Forecasting Models
Streamline enables fine-tuning the models generated by the application in order to make the forecasts best meet your needs. This fine-tuning can be carried out by changing the model type, model coefficients, or increasing/decreasing the model output.
Adjusting the Model Type
There are several types of forecasting models in Streamline:
Each of them is intended to serve a particular purpose. Streamline automatically selects the most appropriate model type for each planning item when forecasting. However, the automatic selection can be overridden by choosing a specific type manually.
Model type can be changed at any level of the tree in the Tree view.
To change the model type:
- Go to Demand forecasting tab.
- Select the node in the Tree view.
- Go to the Properties panel > Forecasting tab
- Select the model type in the Model control.
When set manually, a little hand icon  is added to the selected node and all of its children. In this way, all the children inherit the option automatically. A gray version of the icon before the node indicates inheritance of the option from its parent.
is added to the selected node and all of its children. In this way, all the children inherit the option automatically. A gray version of the icon before the node indicates inheritance of the option from its parent.
To update the forecasts based on the new model type, click the Forecast button.
Increasing or Decreasing the Model Output
In Streamline, you can increase or decrease the output of the model. It is useful when you need to adjust all of the model predictions at once, for example, to increase the forecast by 5 percent. This can be done using the Multiplier option of the Forecasting tab.
The option can be set at any level of the tree in the Tree view.
To increase/decrease the model output:
- Go to the Demand forecasting tab.
- Select the node in the Tree view.
- Go to the Properties panel > Forecasting tab.
- Enter the multiplier in the Multiplier option.
As you change the Multiplier option, a little cross icon  is added to the selected node and all its child nodes. This option is not propagated to the child nodes.
is added to the selected node and all its child nodes. This option is not propagated to the child nodes.
To put the changes into effect, click the Forecast button.
Adjusting Model Coefficients
There are two types of models used to generate forecasts in Streamline: time-series model and the intermittent demand model. They both have their own set of coefficients (or parameters) which can be changed manually. These changes allow performing model fine-tuning at the highest level of detail.
The models consist of components. Each component has its own weight that determines the component contribution to the model predictions. The model coefficients are those weighs.
Model coefficients can only be changed at the lowest level of the Tree view.
To change a model coefficient:
- Go to the Demand forecasting tab.
- Select the node in the Tree view.
- Go to the Properties panel > Model tab.
- Click the yellow cell of the Coefficient column corresponding to the component.
- Enter a new value and press Enter.
To revert to the original value, just clear the adjustment.
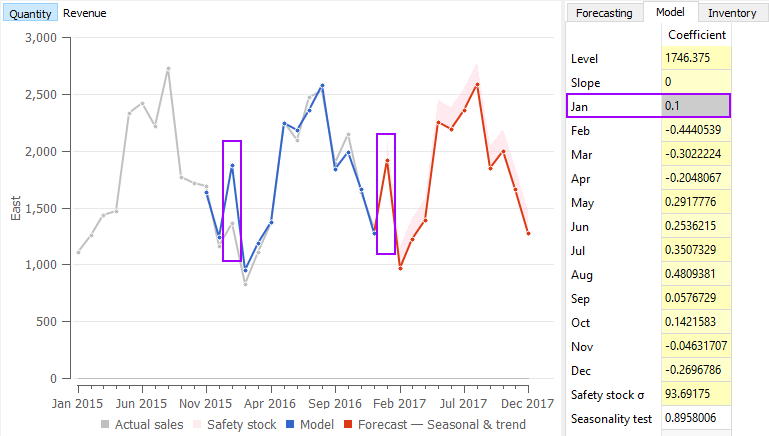
Example
Consider the time-series model. It consists of the Level and Slope components, and the Seasonal components corresponding to the twelve months. Let’s increase the coefficient of the January seasonal component from -0.28 to 0.1. The model output is updated immediately as the change is made. It is shown in the Plot view.